5.5-5.6 Legal/Ethical Concerns and 5.6 Safe Computing
Notes and hacks on computing bias and crowd sourcing.
5.5 Legal and Ethical Concerns
- Software companies make money by getting patents for their code and selling them to hardware companies (paying a royalty payment).
- “Black Duck® = helps teams manage the security, quality, and license compliance risks that come from the use of open source and third-party code in applications and containers.”
License Types
- Creative Commons Zero = waives compyright interest in a work created and dedicates it to the world-wide public domain
- Open source MIT License = the author of software with MIT License want credit (ex. adding author name in comments)
- Open Source GPL License = lets people do almost anything they want with your project, except distributing closed source versions (can’t sell it) ^ Companies will split code to sell the closed patented code and give the open code to customers to piece back together
Legal and Ethically
- we often violate Digital Rights Management = downloading music, movies, and other content from illegal websites that have bybassed the systems
- creative commons = open source code that lets us learn a lot for free
Reflection
-
Github License Types when creating a repository:
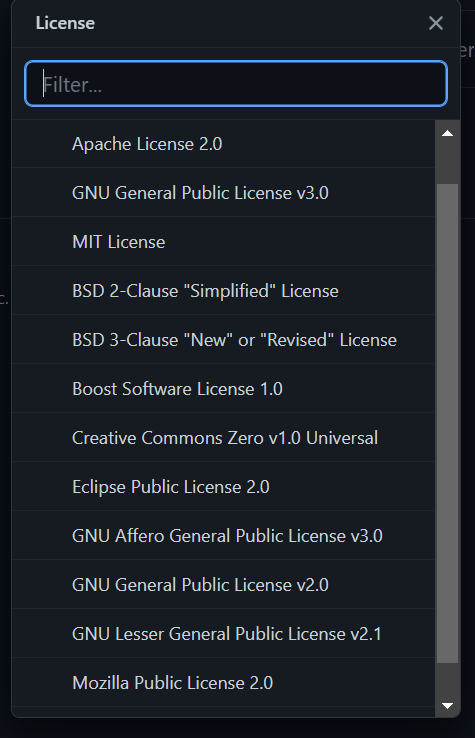
- I see many public and universal licenses. These licenses are likely open source code that anyone can access such as the MIT license that just requires credit.
- I see a “new” and “revised” license that likely lets someone update a patent.
- There is a Boost Software License that may be a closed source license but I am not sure.
- I assume all of these licenses offered by Github are for making your work public, just requiring some sort of credit when used (maybe different levels of open).
-
There are many different licenses you can get for your code depending on your team’s goal. There are open source and closed source code that allow you to share/access code for free or you can sell your code for royalty pay. I think patents are great for giving credit to those who invented/created content/code/program. Look at notes above for more information/summaries.
-
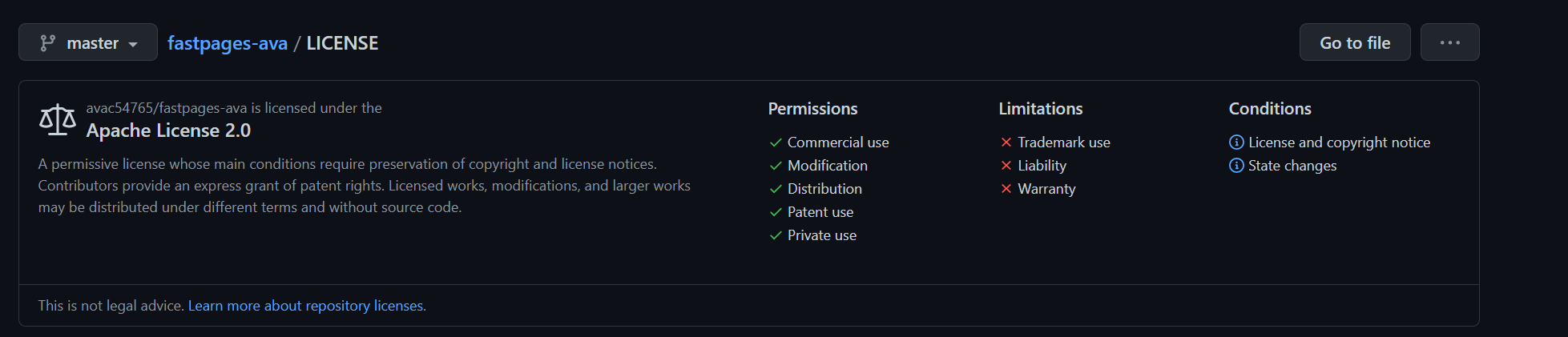
Creating Licenses for repos:
- personal:
- team frontend repo:
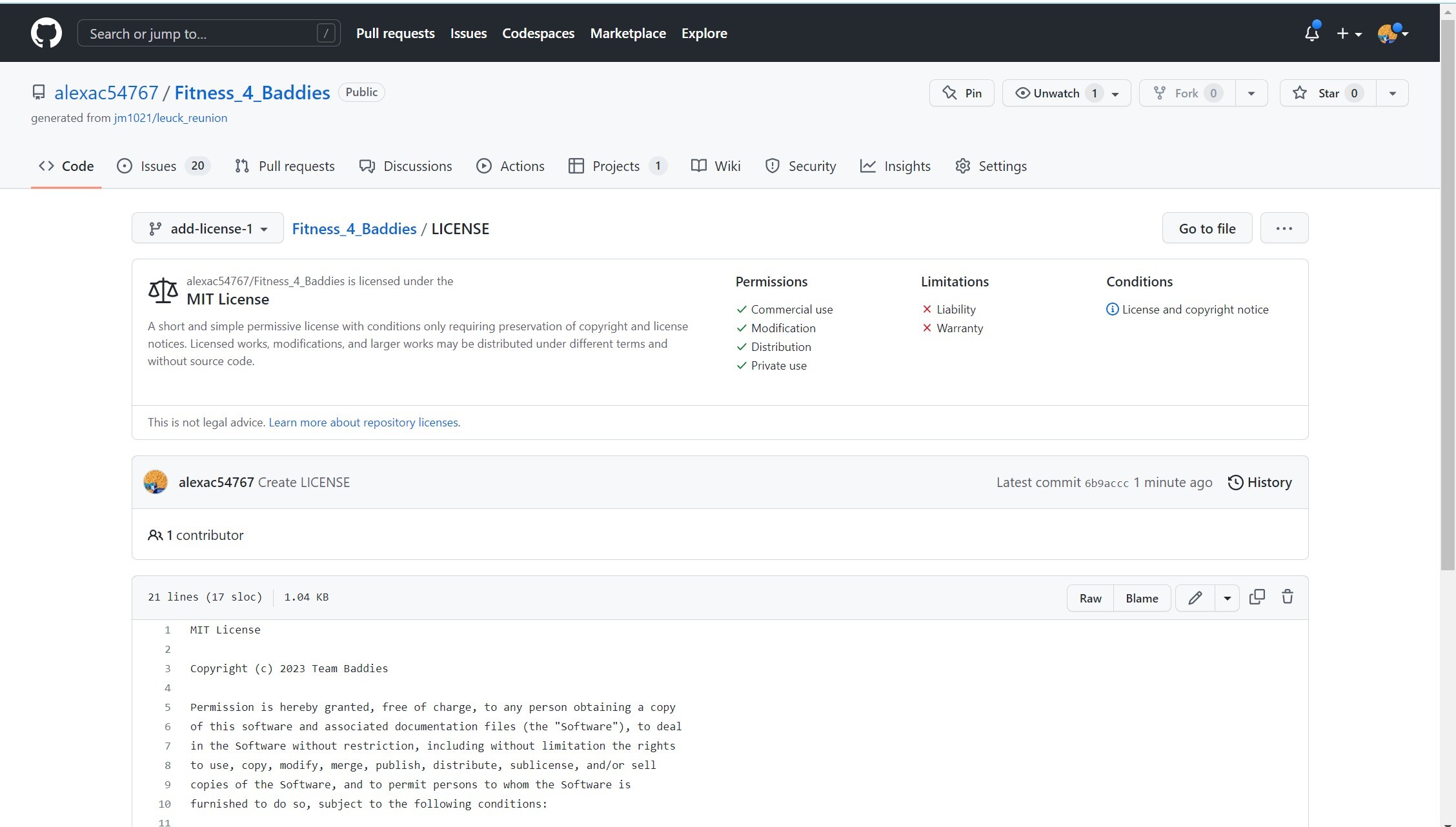
- team fastpage repo:
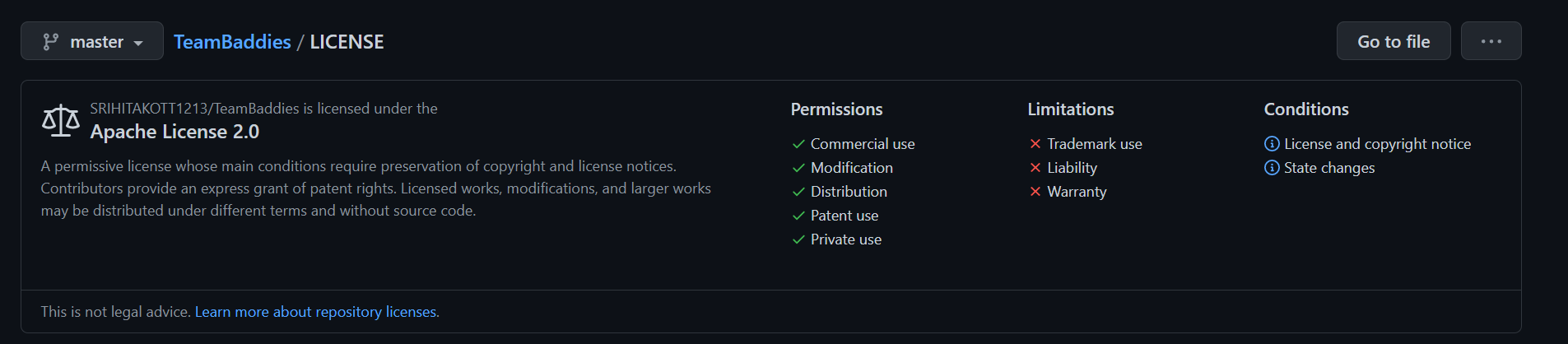
-
team flask repo:

- My team chose the MIT license for all of our repositories but one because the MIT License allows for commercial use, modification, distribution, amd private use but limits liability and warranty. Users are also required to give credit to us when using our code. This means that anyone is allowed to use our code, but we will not get in trouble if the code causes an issue/damage, and we will still be credited for our code contributions (to help the ego yk).
- For our Team Fastpage, (where we have team blogs, planning, and presentations) there was already in existing license for the Apache License 2.0. Our team decided to leave this license because it is similar to the MIT license, but also limits trademark use. This means that someone cannot trademark our work, causing us to not be able to use it.
- How we changed our repository licenses. We referenced this link, which taught us how to add a license file and select the type of license we would like.
5.6 Safe Computing
- PII= Personal Identifiable Information
- acceptable PII = name, email, picture, high school, college, residence, etc.
- grey area = birthday, birthplace, street address, number, drivers license, etc.
- secret: access credentials, financial accounts, social security number, tax records, etc.
- RECOMMEND: use multi-factor authentication, symmetric encryption (one key), DON’T click on random attachments/phishing that will ask you to log in/install malware
Reflection
- PII I have seen in Computer Science Principals include names, Github usernames, repositories, Github activity, Twitter profiles, Youtube profiles, emails, and pictures. Github profiles give a lot of information about someone and as students in this class, we all of Github accounts. Any link for contact on Github repositories is also PII.
- When it comes to PII, there is some information that I feel is okay to expose, but other information I would be greatly concerned about if leaked. I think it is okay to have my name, email, and maybe picture out for the world to see. Although, I would want to keep my number, credit card information, and passwords all away from other people’s knowledge. Others attaining this information could do some pretty bad things to me.
- Good passwords are long in length, have different types of characters, and do not have your name in them. Bad passwords are short, easily guessable, and have very limited combinations that the password could be. Another step that is used to assist in authentication is when a code is sent via email or text to ensure it is in fact you trying to login.
- Asymmetric Encryption is a process of sending data to someone that is encrypted. A public key is used to encrypt the data, but a private key is needed to decrypt the data. Symmetric Encryption is the same as Asymmetric Encryption, except only a single key is needed to encrypt and decrypt the data. Generally, Asymmetric Encryption is safer than Symmetric Encryption.
- In AWS deployment, we used encryption keys when first creating our repository. We used SHH deployment keys, one public and one private (asymmetrical), and copied and pasted them into our Github.
- Normally I am pretty good about not falling for phishing schemes, but on scheme that I learned the hard way from was an email from apple that seemed legit. The email was talking about some apple update or something that required me to sign into my Apple account. I ended up doing it because the site looked legit. I then soon realize that the website was a phishing scheme and I change my Apple ID password. Other phishing techniques include bank account alerts/texts, prize-winning emails/calls, and Instagram messages that say something like ‘I need your help” or “I made this for you”.