Live Review 2-3 Vocabulary and Examples
Vocabulary for lessons
Live Review 3 Vocabulary and Examples
- Binary Numbers: a numbering scheme in which there are only two possible values for each digit – 0 or 1 – and is the basis for all binary code used in computing systems
-
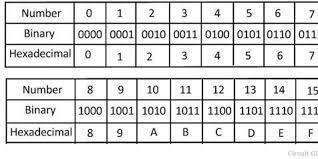
Hexadecimal: a numbering system with base 16
-
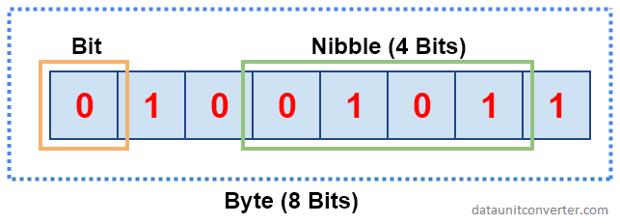
Bits: the smallest unit of data that a computer can process and store
- ex: 1 or 0 (one number in binary is a bit)
-
Bytes: a unit of data that is eight binary digits long
- ex: 10010110
-
Nibble: four consecutive binary digits or half of an 8-bit byte
- ex: 0101
- ex: 0101
-
Unsigned Integer: integers but have the property that they don’t have a + or - sign associated with them
- ex: 2, 3, 6, 1000
-
Signed Integer: integers that have a + or - sign associated with them
- ex: -2, +3,000, -1
-
Floating Point: a positive or negative whole number with a decimal point
- ex: 3.25, 5.1, 67.627
- Binary Data Abstractions:
-
Boolean: a logical data type that can have only the values true or false

- ASCII: (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) a standard code for characters stored in a computer or to be transmitted between computers
- Unicode: a universal character encoding standard
-
RGB: a system for representing the colors to be used on a computer display

-
Data Compression: a reduction in the number of bits needed to represent data
- Lossy: data encoding and compression technique that deliberately discards some data in the compression process
-
Lossless: restores and rebuilds file data in its original form after the file is decompressed

Live Review 2 Vocabulary and Examples
-
variables: “containers” or used to store information to be referenced and manipulated in a computer program
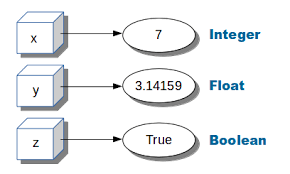
- data types: a classification that specifies which type of value a variable has and what type of mathematical, relational or logical operations can be applied to it
-
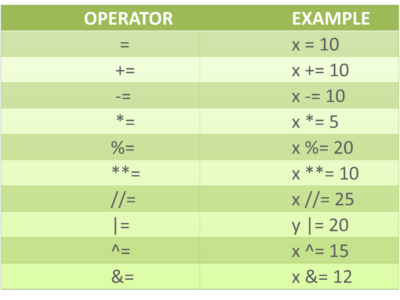
assignment operators: the operator used to assign a new value to a variable
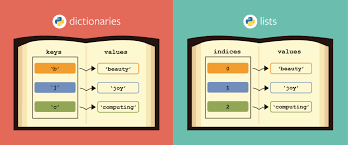
- lists: an abstract data type that represents a finite number of ordered values
-
dictionaries: an abstract data type that defines an unordered collection of data as a set of key-value pairs
-
class: a template definition of a method and variable in a particular kind of object

- algorithm: a procedure used for solving a problem or performing a computation
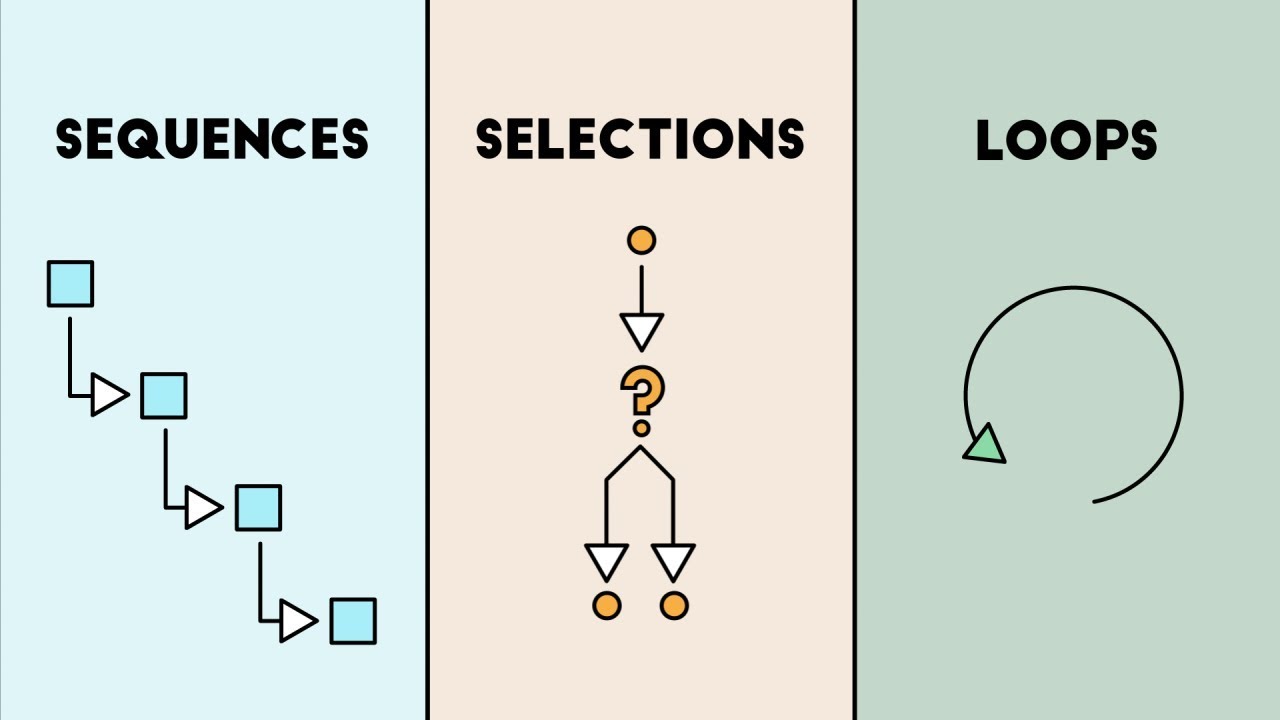
- sequence: the order of how to do something to achieve a result
- selection: allows an algorithm to make a decision based on if a condition is met
-
iteration: iteration: a loop and doing something again until a condition is met
- expressions: a concept in which a number of variables or constants, and operators and functions, are put together in a single statement that is acted on by a particular programming language
-
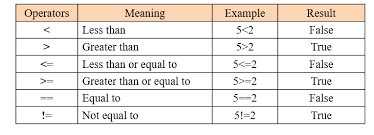
comparison operators: compare the values within an expression, such as to check if the value held by a variable matches the value held by another variable
- boolean expression: a logical statement that is either TRUE or FALSE
-
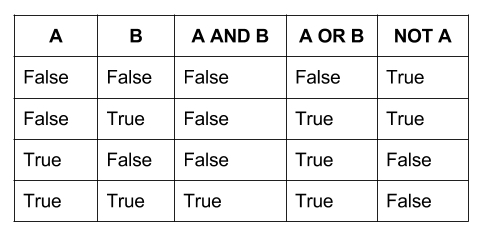
truth tables: a breakdown of all the possible truth values returned by a logical expression (usually 1/0, true/false)
- characters: a display unit of information equivalent to one alphabetic letter or symbol ex. a
- strings: an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements ex. “apple”
- length: length() function returns the number of items in an object
- concatenation: the operation of joining two strings together (joined by plus sign)
- python if: a conditional statement tha decides if a certian condition is true/decides whether certain statements need to be executed or not
- python elif: elif = else if and checks for multiple expressions (if the condition for if is False, it checks the condition of the next elif block)
-
python else conditionals: else catches anything which isn’t caught by the previous conditions (like and if statement)

- nested selection statements: when more than one decision must be made before carrying out a task
- Python for loop: a control flow statement that is used to repeatedly execute a group of statements as long as the condition is satisfied
- Python while loop with range and with list: sets aside a block of code that is to be executed repeatedly until a condition is falsified ex. while i == 0
- Procedural Abstraction: when we create code sections which are generalised by having variable parameters (more simple)
- paramerters: a special kind of variable used in a function to refer to one of the pieces of data provided as input to the function ex. function(parameter)
-
return values: a value that a function returns to the calling function when it completes its task